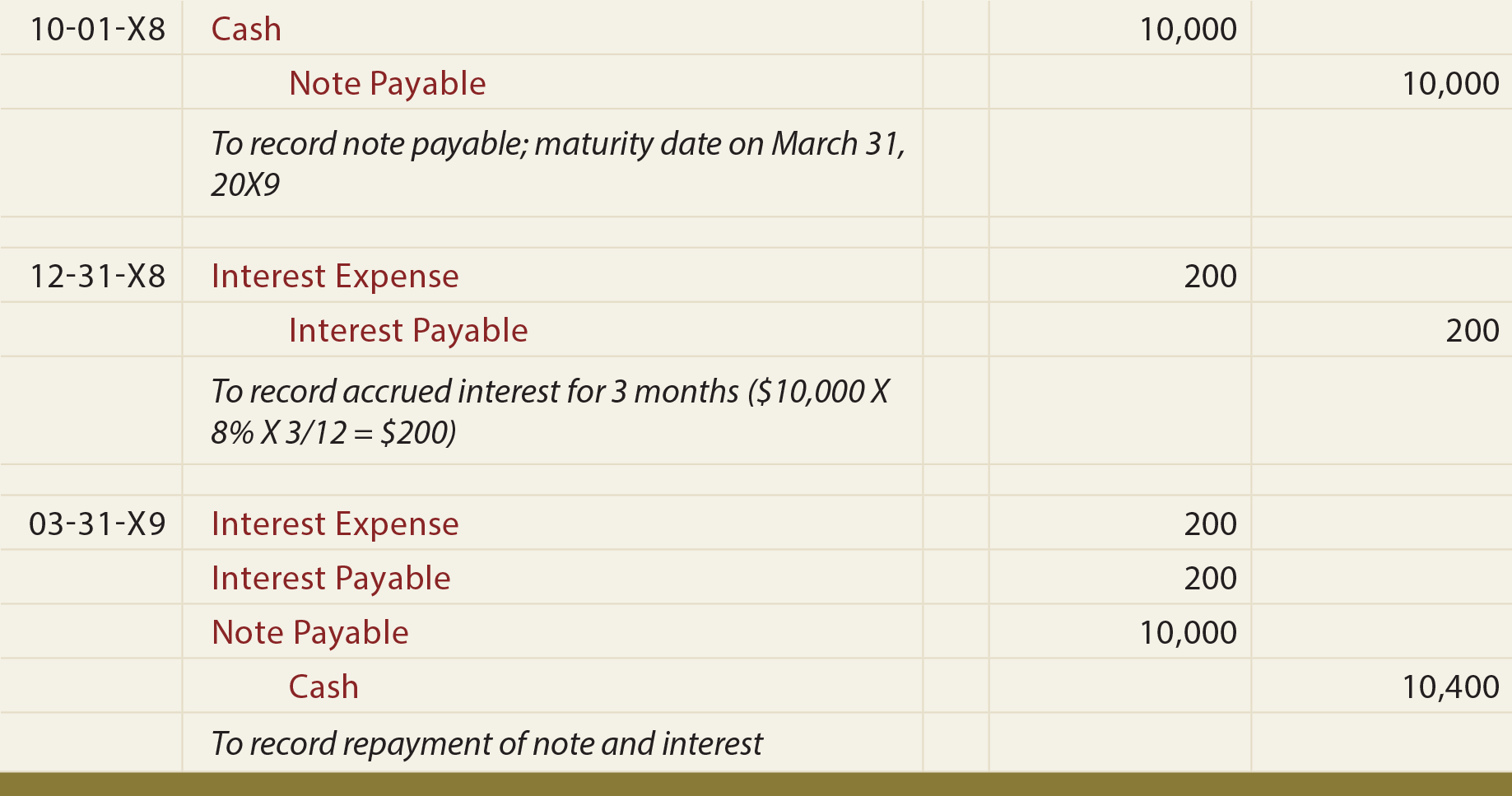
Your company receives a $10,000, 4 year, 2% annual interest note, paid semi-annually. The payee is the party who receives payment under the terms of the note, and the maker is the party obligated to send funds to the payee. The amount of payment to be made, as listed in the terms of the note, is the principal. This adjusting journal entry is needed to conform to GAAP, recording revenue in the month it is earned. Since cash isn’t changing hands until later, we record the amount in the Interest Receivable account to keep track of what will be due. But, briefly, if a bank is loaning cash (the bank’s Note Receivable) to a customer (the customer’s Note Payable), the credit would be to Cash for the bank.
What is an Asset?
This is because not all the sales made to a particular customer are recorded in the customer’s subsidiary accounts receivable ledger. The note has now been completely paid off, and ABC has recorded a total of $246 in interest income over a three-month period. Accruing state unemployment insurance sui rates tax liabilities in accounting involves recognizing and recording taxes that a company owes but has not yet paid. This is important for accurate financial reporting and compliance with… The $18,675 paid by Price to Cooper is called the maturity value of the note.
Interest Rate
- The difference between a short-term note and a long-term note is the length of time to maturity.
- Notes receivable refers to a written, unconditional promise made by an individual or business to pay a definite amount at a definite date or on demand.
- For this reason, both IFRS and ASPE allow net realizable value (the net amount expected to be received in cash) to approximate the fair value for short-term notes receivables that mature within one year.
- Together, the principal and interest portions represent the note’s maturity value.
- For example, if the interest rate (I/Y) is not known, it can be derived if all the other variables in the equation are known.
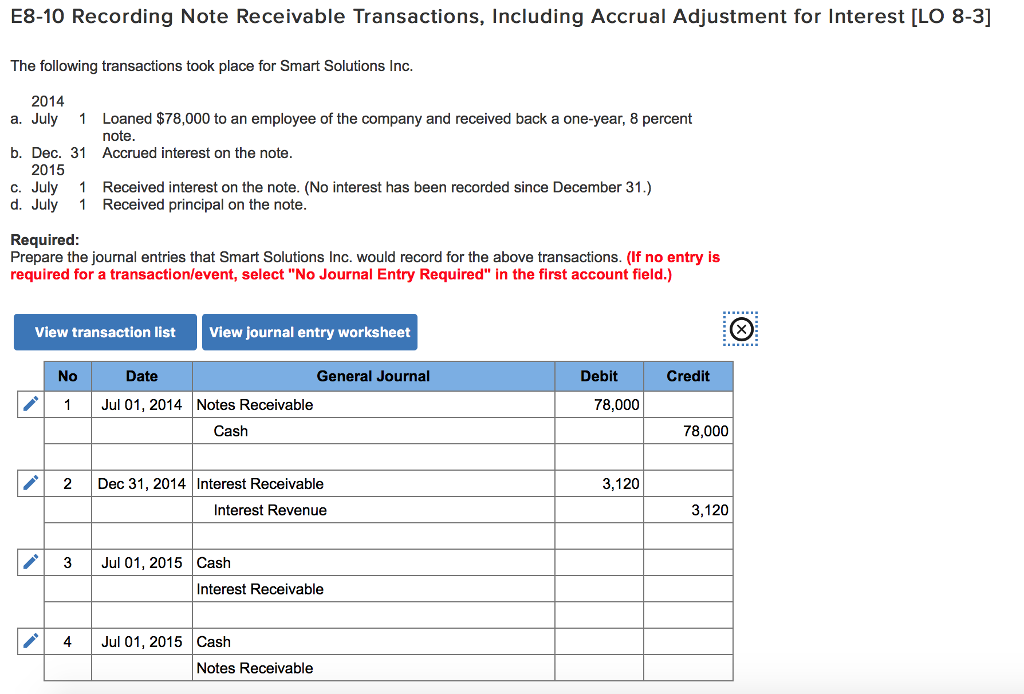
In this article we dive into an example of how to do a Notes Receivable calculation, using both IFRS and ASPE methods.
Accounting in the Headlines
Interest Income or Interest Revenue is an Revenue account so it has a normal credit balance. Interest Income or Interest Revenue is increased on the credit (right) side of the account and decreased on the debit (left) side of the account. The account name used will be specified in the company’s Chart of Accounts. A Note Receivable is recorded when a company is on the “receiving” side of a debt.
This difference would be deemed as additional compensation and recorded as Compensation expense. The implied interest rate is calculated to be 5% and the note’s interest component (rounded) is $2,165 (), which is the difference between the cash lent and the higher amount of cash repaid at maturity. Below is the schedule for the interest and amortization calculations using the effective interest method. A note receivable is a promissory note made by a maker to a payee promising to repay a specified amount at a future time. However, the accounting entry will follow if the company converts an accounts receivable balance to a note receivable. Finally, a note receivable will also mention the timeframe of the loan.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
On 1 May 20X4, PQR, Inc. lent $2 million to ABC, LLC for 2 years against a documented promissory note. DEF, Inc., another client of PQR, Inc. issued a 2-month promissory note against their outstanding balance of $3 million on 1 November 20X4. Note receivable from ABC LLC carried 5% simple interest rate payable annually while the one from DEF Inc. carried 8% interest compounded monthly.
Notes receivable also arise when a business lends an amount to another party against a documented promise to pay it back. The difference between a short-term note and a long-term note is the length of time to maturity. As the length of time to maturity of the note increases, the interest component becomes increasingly more significant. As a result, any notes receivable that are greater than one year to maturity are classified as long-term notes and require the use of present values to estimate their fair value at the time of issuance. After issuance, long-term notes receivable are measured at amortized cost.
Interest Receivable decreasing (credit) reflects the 2018 interest owed from the customer that is paid to the company at the end of 2019. The second possibility is one entry recognizing principal and interest collection. Interest on a note receivable is calculated by multiplying the principal balance of the note by the interest rate and by the number of days that have elapsed since the last interest payment was made divided by 365. With a promissory note, the third party who issued the note (called the maker) promises in writing, to pay an amount of money (principal and interest) to the business (called the payee) at a given time or on demand. The accounting treatment of interest that is accrued but remains unpaid up to balance sheet date, depends on whether the interest is compound or simple.
At the maturity date of a note, the maker is responsible for the principal plus interest. The payee should record the interest earned and remove the note from its Notes Receivable account. Thus, the payee of the note should debit Accounts Receivable for the maturity value of the note and credit Notes Receivable for the note’s face value and Interest Revenue for the interest.
Sometimes a company receives a note when it sells high-priced merchandise; more often, a note results from the conversion of an overdue account receivable. When a customer does not pay an account receivable that is due, the company may insist that the customer gives a note in place of the account receivable. This action allows the customer more time to pay the balance due, and the company earns interest on the balance until paid. Also, the company may be able to sell the note to a bank or other financial institution.
Notes receivable refers to a written, unconditional promise made by an individual or business to pay a definite amount at a definite date or on demand. On March 31 a similar entry will be made to record the interest revenue earned in March. On February 28 a similar entry will be made to record the interest revenue earned in February. In this journal entry, the Accounts Receivable invoice for Dino-Kleen is reduced to take the invoice out of Accounts Receivable. It will no longer appear on Accounts Receivable reports or be included in the Accounts Receivable total.

Commenti recenti